Documentation
Documented information about the entire RuneScape game.
Data Types
RuneScape uses a number of uncommon and bespoke data formats to obsfuscate communication and reduce cache file size.
Each client revision randomises the endianness and modifications used for decoding client packets. The OSRS protocol scrambling follows a decipherable order (citation needed).
Standard Java Data Types
RuneScape client uses Java’s primitive data types to store and transmit information, understanding these limitations and sizes are important regardless of client revision.
| Type | Size | Minimum Value | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| byte | 1 byte | -128 | 127 |
| short | 2 bytes | -32,768 | 32,767 |
| int | 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 | 2,147,483,647 |
| long | 8 bytes | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 | 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
| float | 4 bytes | ||
| double | 8 bytes | ||
| boolean | 1 bit | false | true |
| char | 2 bytes | 0 | 65535 |
2,147,483,647 is the maximum stack a player can have of one item because item amounts are stored as integers.
Signed and unsigned
Data types typically are Signed, easily thought of as a single bit assigned as a binary flag denoting a positive or negative number. However when only positive values are necessary the flag can be unsigned allowing a larger number to be stored in the same amount of space.
| Type | Size | Minimum Unsigned Value | Maximum Unsigned Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| byte | 1 byte | 0 | 255 |
| short | 2 bytes | 0 | 65,535 |
| int | 4 bytes | 0 | 4,294,967,296 |
| long | 8 bytes | 0 | 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 |
Methods utilising unsigned integers commonly use ‘U’ as a prefix e.g.
readUByte
Bit Access
The client also utilises reading and writing individual bits interchangeably with other data types.
TODO code example needed for both read and write which cleanly breaks down how it works
Obfuscation methods
Endianness
The read and write order of byte data is called Endianness RuneScape client occasionally uses a middle-endian (integer’s only) the order of which is determined by an inverse modification.
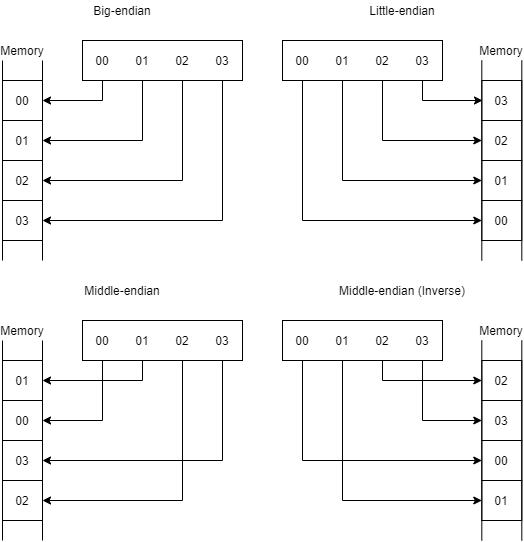
- Big - Most significant bit first
- Little - Least significant bit first
- Middle - Most significant bit central
Modifications
Several further modifications can be made to bytes before and reversed afterwards as obfuscation
| Name | Read | Write |
|---|---|---|
| A | value - 128 |
value + 128 |
| C | -value |
-value |
| S | 128 - value |
128 - value |
Implementation
Kotlin (bespoke type support needed)
Bespoke types
Medium/Tribyte
A custom data type for storing 3 byte numbers between -8,388,608 and 8,388,607
Smart
Functions that “smartly” choose the smallest data type necessary to store the value provided
e.g
if value < byte max
write byte
else
write short